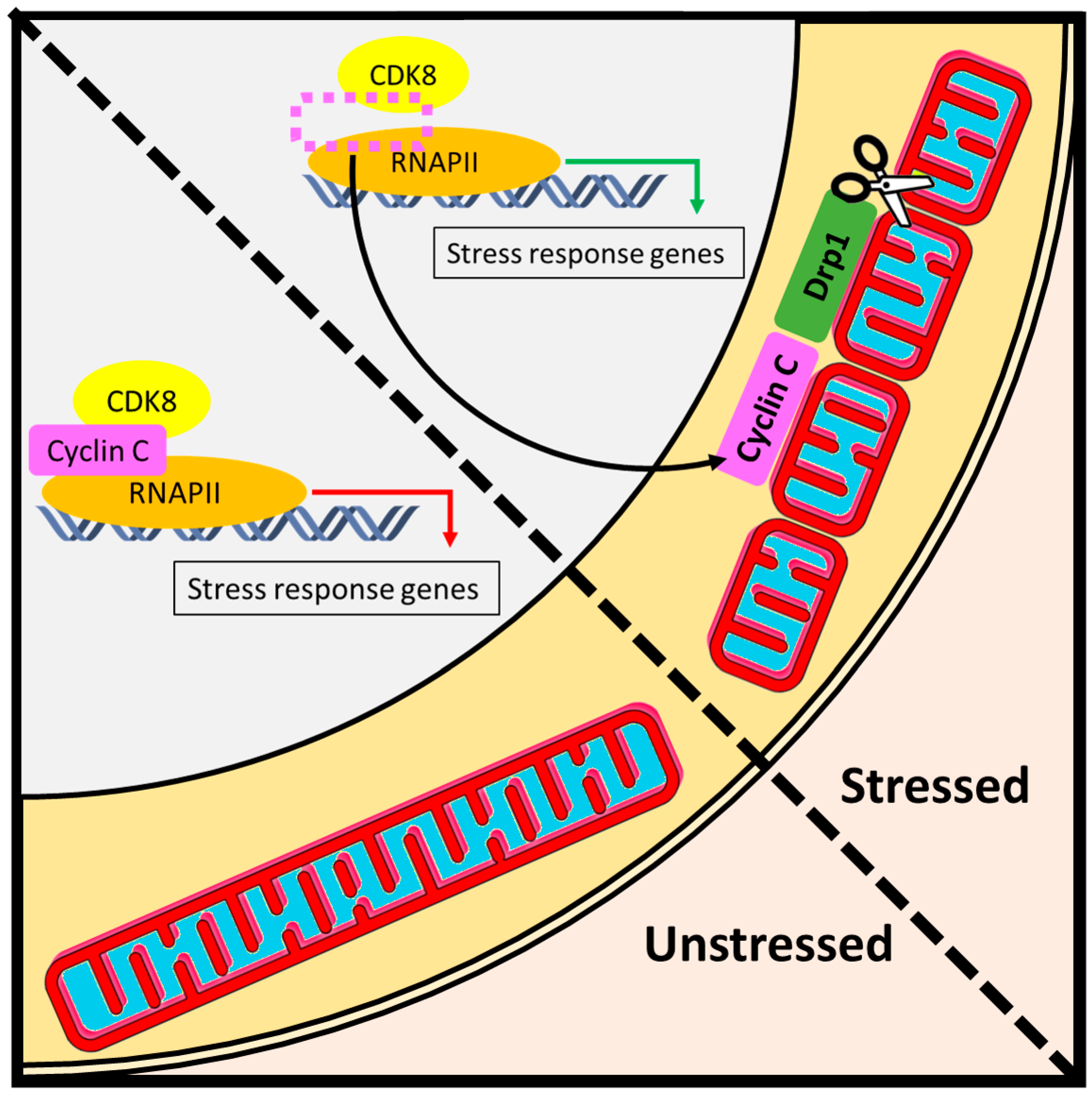
Cell Growth Control Lab Biology Diagrams Thus, the cyclin and cdk are the proteins that are responsible for guiding cells from one phase of the cell cycle to the next. Cyclins: Types and Regulation in Cell Cycle Control. Cyclins are proteins which binds to enzymes called cyclin dependent kinases (CKD). Many types of cyclins exist which bind to different types of CKDs.

Cyclins function as regulatory proteins that control the progression of the cell cycle. They bind to cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and activate them, allowing the CDKs to phosphorylate specific proteins and trigger different cell cycle events. These events include DNA replication, nuclear division, and cell division. What Is The Role Of Cyclin D?
Cell cycle, Checkpoints, Cyclins and Its Types: Introduction, External ... Biology Diagrams
Cyclin Dependent Kinases (CDKs) are closely connected to the regulation of cell cycle progression, having been first identified as the kinases able to drive cell division. In reality, the human This division is useful when talking about most cell cycles, but it is not universal as some cyclins have different functions or timing in different cell types. Protein cyclin A governs this process by keeping the process going until the errors are eliminated. In normal cells, persistent cyclin A expression prevents the stabilization of
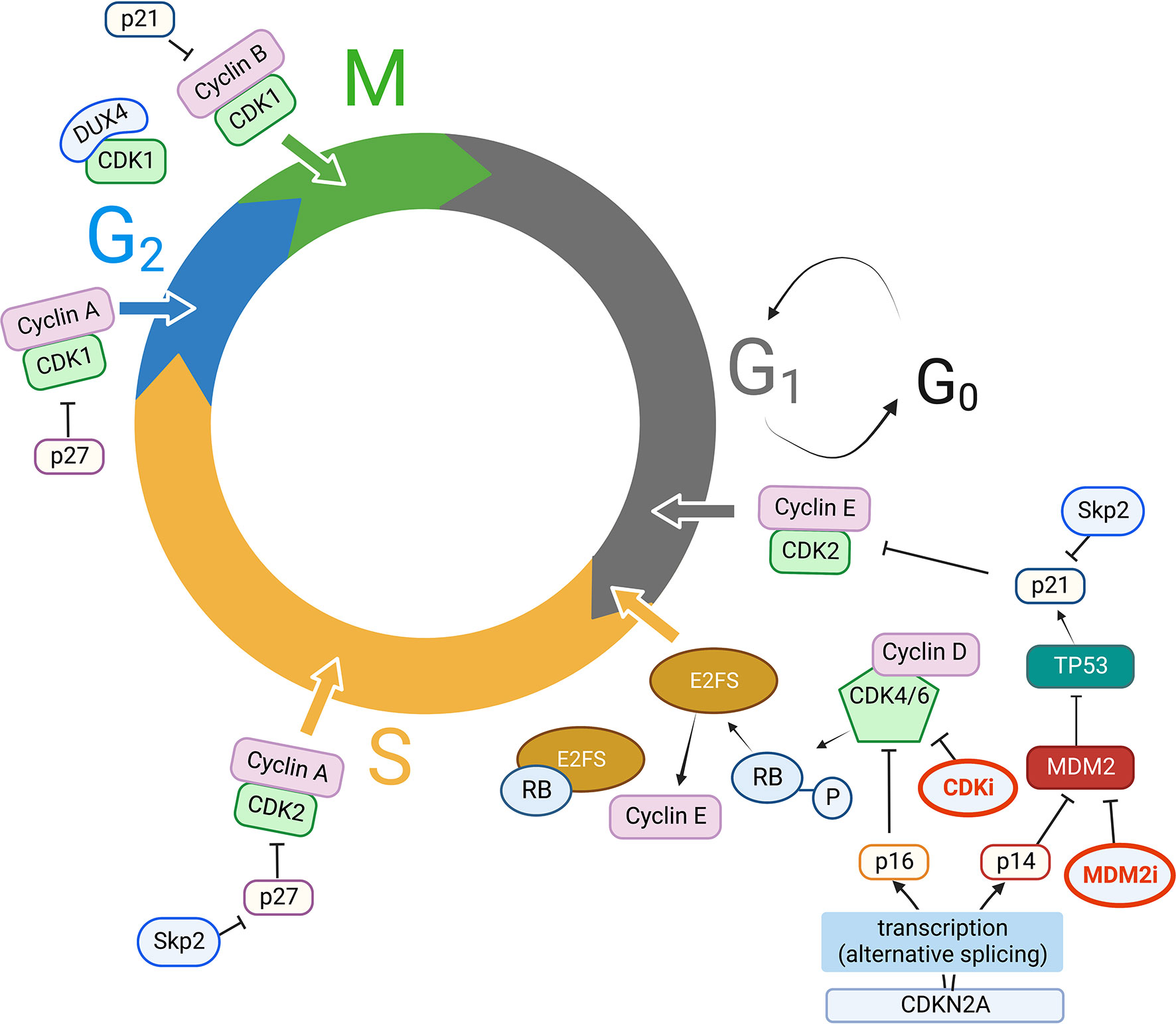
Next, CDK2/cyclin E function is inhibited and on G 1 cyclin-dependent kinases inhibition, proteins that belong to the retinoblastoma protein family are turned back to their hypophosphorylated active state and cells exit the cycle . Figure 3.
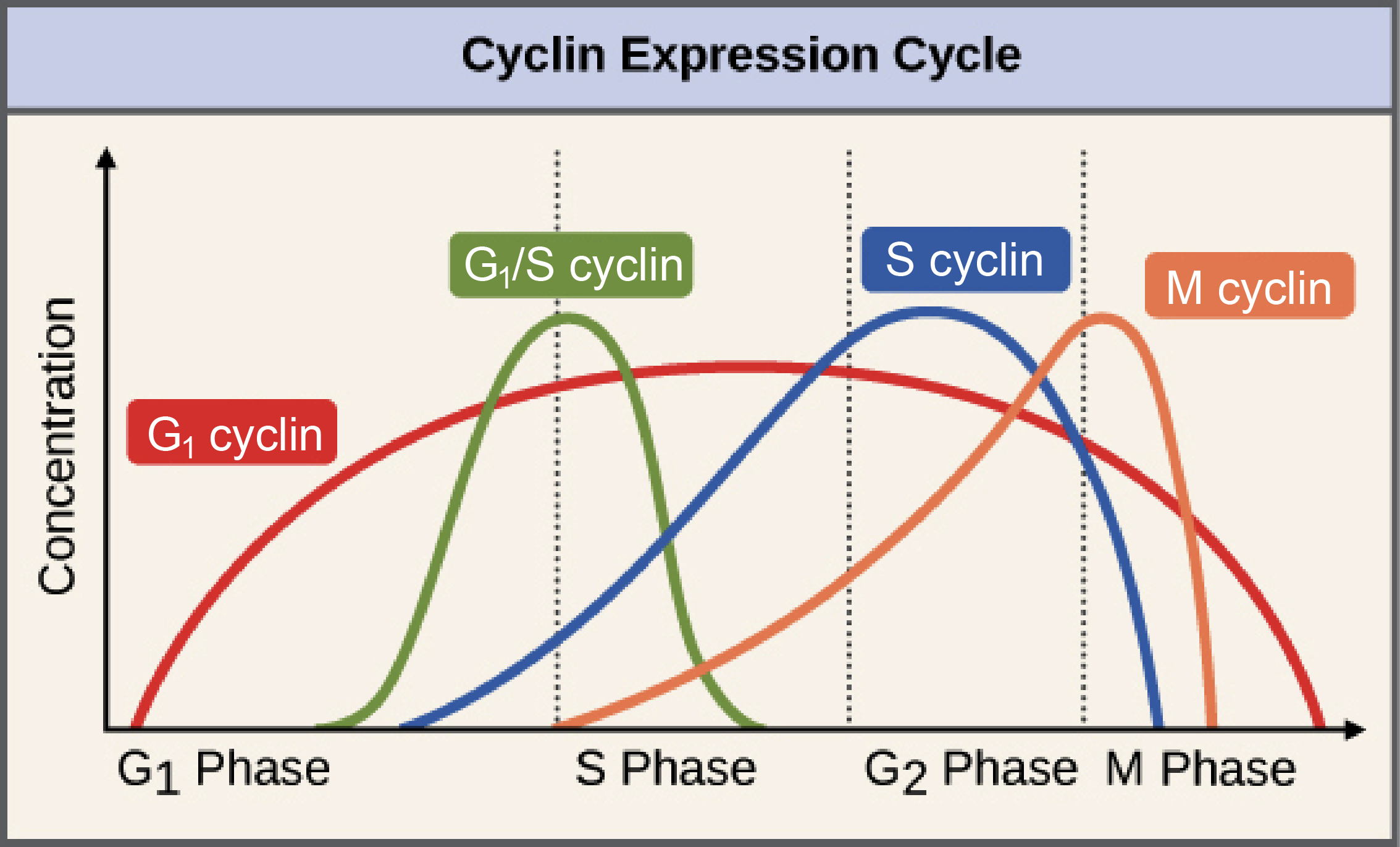
Biology Simple Biology Diagrams
The TFIIH complex, which is a component of a 10-subunit general transcription factor, consists of the regulatory subunit cyclin H, the catalytic subunit CDK7, and a ring finger protein menage a trois 1 (Mat1), which functions as the helicase, ATPase, and protein kinase; it is also the last to be recruited. Another example of a target protein is the phosphorylation of p27, which usually functions to inhibit Rb. Phosphorylation by CDK-2-cyclin E complex prevents this inhibition and so progression from