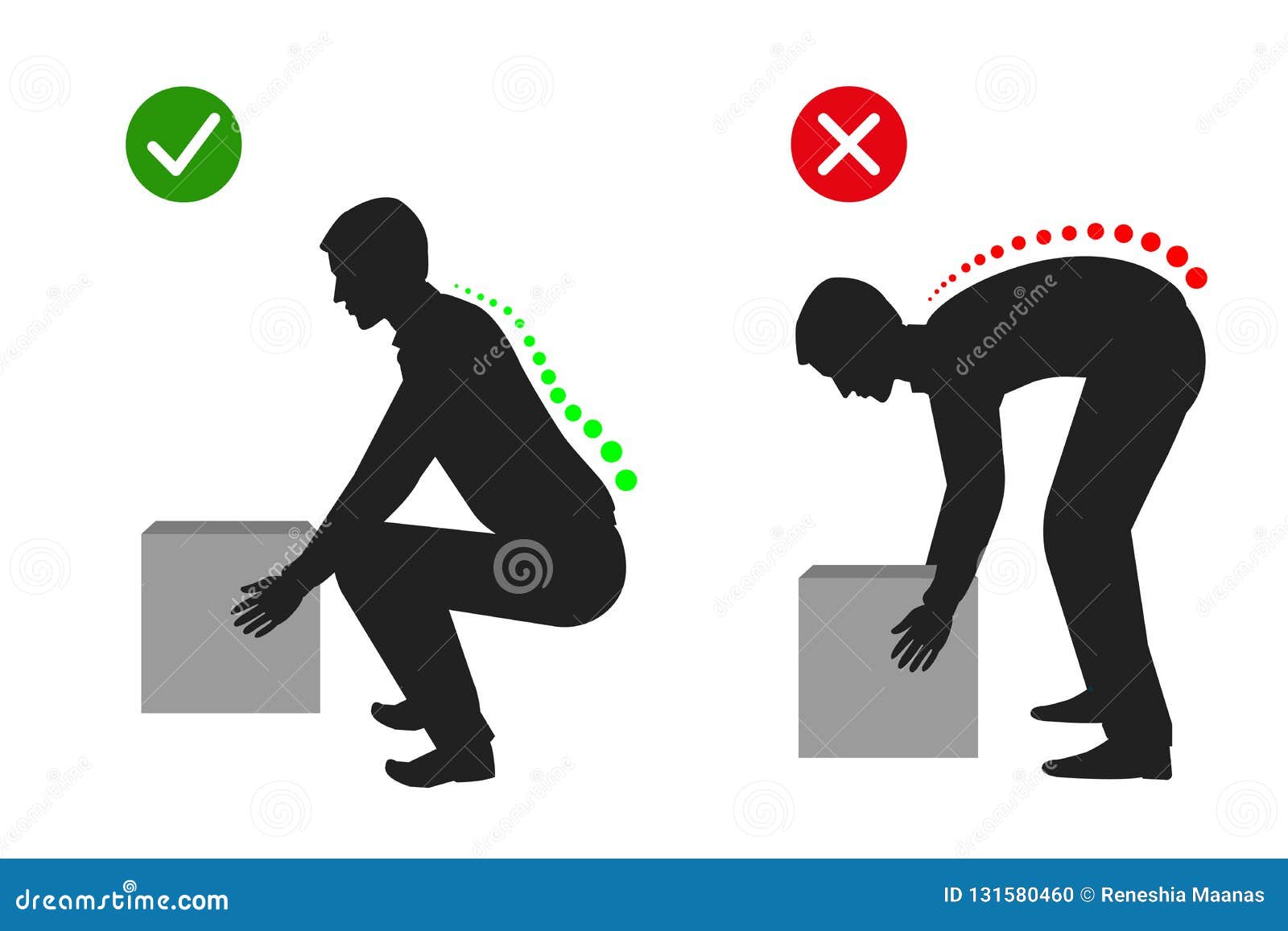
dreyfuss ergonomics Google Search Biology Diagrams Human factors engineering is relevant in the design of such things as safe furniture and easy-to-use interfaces to machines and equipment. Proper ergonomic design is necessary to prevent repetitive strain injuries and other musculoskeletal disorders, which can develop over time and can lead to long-term disability.Human factors and ergonomics are concerned with the "fit" between the user

The terms ergonomics and human factors can be used interchangeably. The latest formal definition of Ergonomics is: "Ergonomics (or human factors) is the scientific discipline concerned with the understanding of the interactions among human and other elements of a system, and the profession that applies theory, principles, data and methods to It is the study of designing equipment and devices that fit the human body and its cognitive abilities. The areas of emphasis are: Physical Ergonomics, Cognitive Ergonomics, and Organizational Ergonomics. 6.1. Ergonomic Basics 6.1.1. Focuses of ergonomics 6.1.2. Ergonomics and its areas of application in a work system 6.1.3. Ergonomic interventions

PDF 6. Ergonomics and Human Factors Biology Diagrams
The field of human factors and ergonomics is interdisciplinary, with applications wherever humans interact with equipment in a system's context. Examples will be drawn from a wide range of work contexts, including medicine, transportation, and computer tasks. The course begins with core topics from anatomy, kinesiology and the physiology of Ergonomics (or human factors) is the scientific discipline concerned with the understanding of interactions among humans and other elements of a system, and the profession that applies theory, principles, data and methods to design in order Physical ergonomics is concerned with human anatomy, and some of the anthropometric, physiological Anatomy in Ergonomics: Ergonomics is rooted in the understanding of human anatomy and physiology. [1] Designing workspaces that consider the natural movements and limitations of the human body can significantly reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and other health issues associated with prolonged sitting or repetitive tasks. From chair

It brings together knowledge from anatomy and physiology, psychology, engineering and statistics and ensures that the designs complement the strengths and abilities of people who use it. Human factors/ergonomics in eWorld: methodology, techniques and applications. InInternational Conference on Applied Human Factors and Ergonomics 2019 Jul Physical ergonomics considers human anatomical, anthropometric, physiological and biomechanical characteristics as they relate to physical activity (Figure 1.3). The consequences of repetitive motion, vibration, force, working postures and the environment are the most common areas of consideration for physical ergonomics. Other factors include: