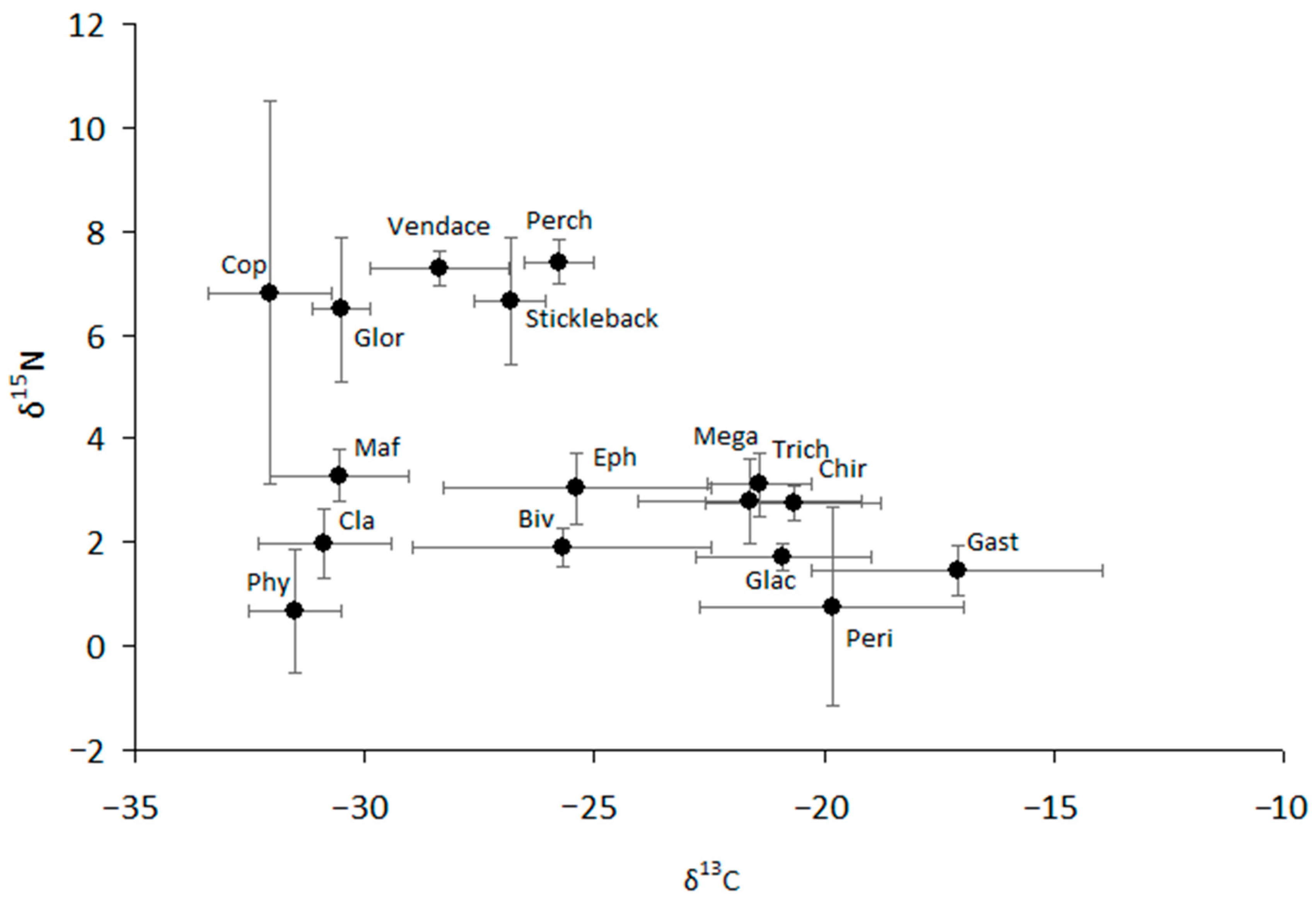
Food Chain Diagram Images Browse 514 Stock Photos Vectors and Video Biology Diagrams Figure 14. Food webs may be described in terms of both energy and nutrient (carbon, nitrogen or phosphorus) flows (Figure 15).Although the process typically begins with sunlight-driven photosynthesis by algae and plants, balanced nutrition is also required to sustain life. For example, we cannot live strictly on sugar, despite its high caloric content, irrespective of what our kids may argue.
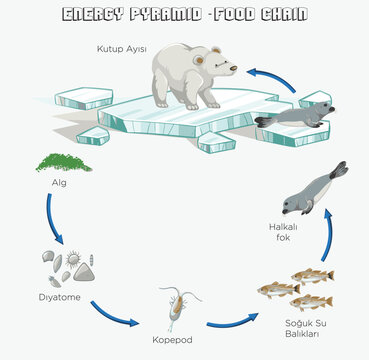
All organisms in those food chains are influenced by non-living (abiotic) factors and living (biotic) factors in their environment. Abiotic conditions (e.g., temperature, pH, clarity, dissolved oxygen, nutrients, etc.) and biotic conditions (e.g., predation, disease, etc.) of the lake impact organisms in the food chain and help to provide a
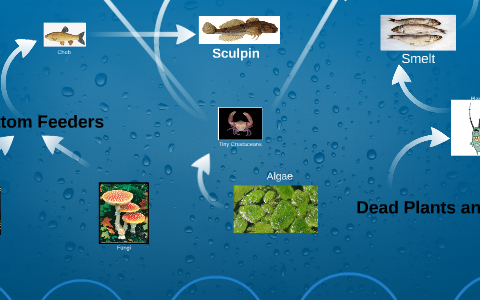
Teaching Great Lakes Science - Michigan Sea Grant Biology Diagrams
Understanding Lake Food Webs: A Deep Dive into Aquatic Ecology. Lakes, seemingly tranquil bodies of water, are bustling ecosystems teeming with life. This intricate system, far from being a simple chain, is a dynamic web of relationships that determines the health and stability of the entire lake environment. Understanding the structure and
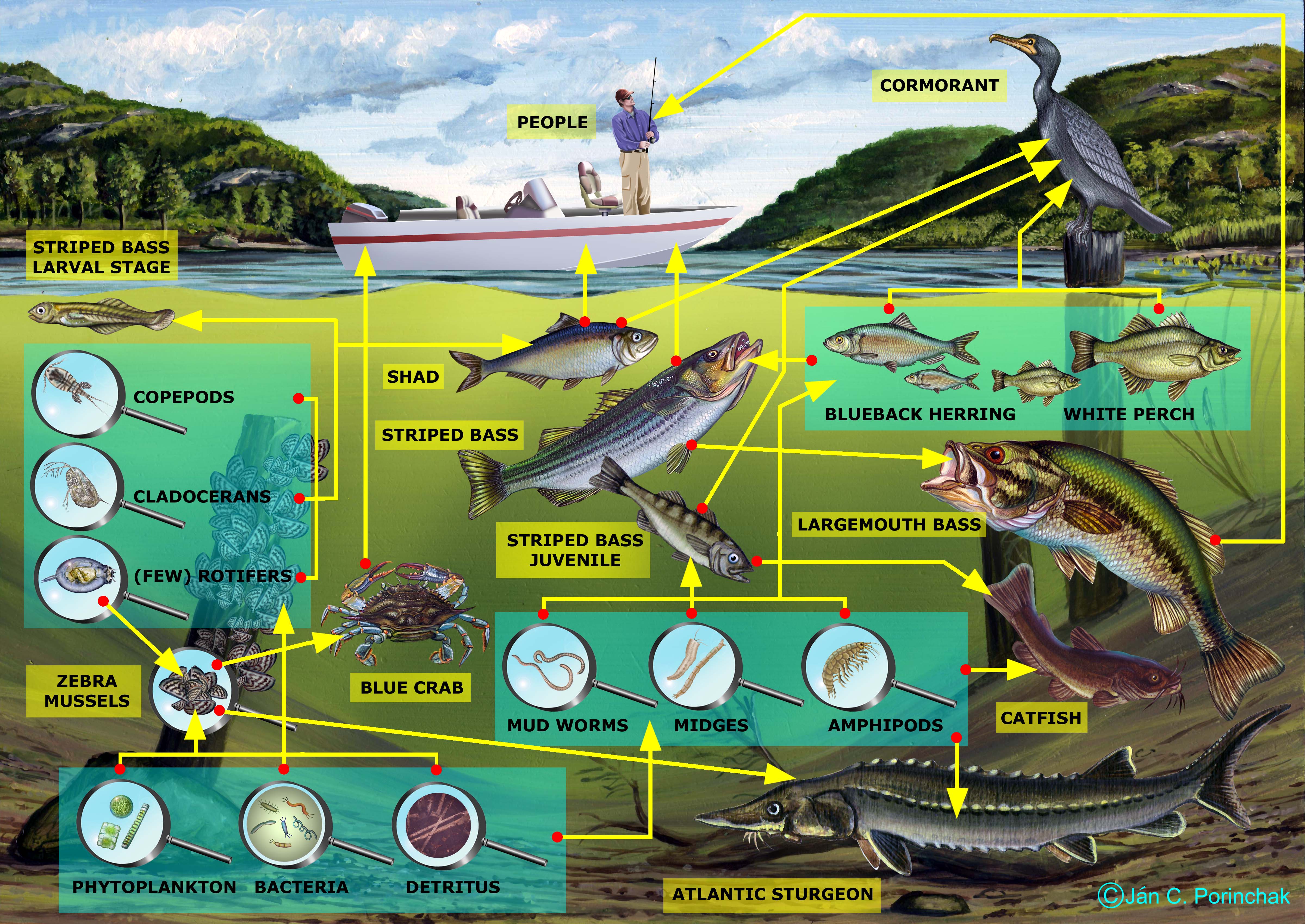
Great Lakes Food Web Diagrams. GLERL has developed food web diagrams for all of the Great Lakes and Lake St. Clair. The major species in each lake are briefly described, along with a diagram summarizing the ecosystem energy flow (who eats or is eaten by whom!). These diagrams are based on a model from a paper published in 2003 supported by both Too few primary producers (phytoplankton, algae and other aquatic plants) and there is not enough food to go up the food chain. Too many primary producers and harmful conditions can occur. For example, dissolved oxygen, an essential ingredient for the survival of almost all aquatic organisms, becomes rapidly depleted as large amount of
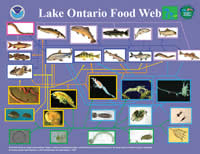
Lake Environment: The Aquatic Food Chain Biology Diagrams
Food chain. A simple introduction to the idea of a lake's food web is to think of it simply as bigger fish eat smaller fish that eat the small floating critters that eat algae, as in the first diagram. Algae are the primary producers, that is, they are able to convert light, nutrients, minerals, and carbon dioxide into organic materials and

Compared to most ecosystems, the Great Salt Lake food web is relatively simple. It is based around two major food chains. The first food chain (on the left side of the diagram) consists of microscopic bottom-dwelling cyanobacteria, brine flies and shorebirds such as gulls.