Food chain Food animals Desert ecosystem Biology Diagrams Kids build a desert food chain, desert food web, and desert food pyramid in this cool science fair project to learn about trophic levels and consumers. the snake, and the hawk. You've created a food chain - a simple line that shows how one small plant can feed a mouse, which feeds a snake, which then feeds a hawk. Creating a Food Web.

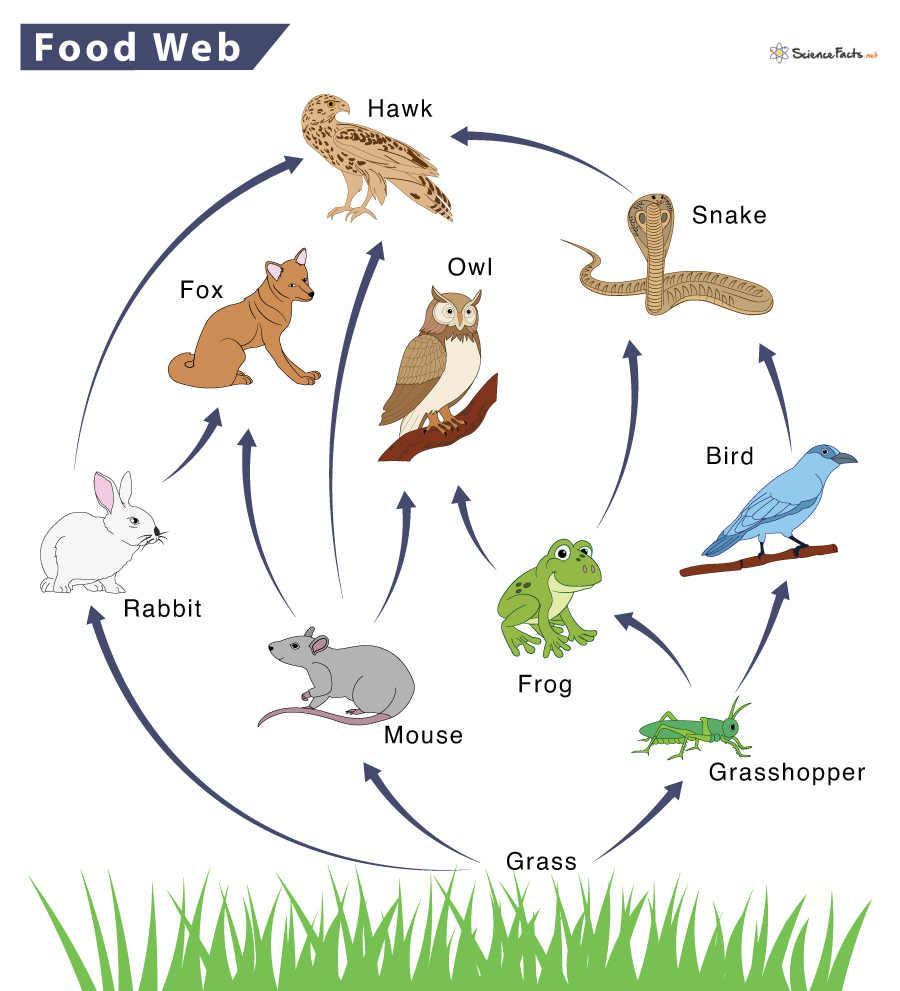
A desert food chain is unique due to its harsh environment. In contrast, the snake is the tertiary consumer in the food chain: Brittlebush -> Grasshopper -> Grasshopper mouse -> Rattlesnake -> Hawk. In the desert, humans are the ultimate predators. Other apex predators compete with humans for food and survival. Food Web: At each trophic level, there may be many more species than indicated in the table above.Food webs can be very complex. Food availability may vary seasonally or by time of day. An organism like a mouse might play two roles, eating insects on occasion (making it a secondary consumer), but also dining directly on plants (making it a primary consumer).
Desert Food Chain: Example and Diagram Biology Diagrams
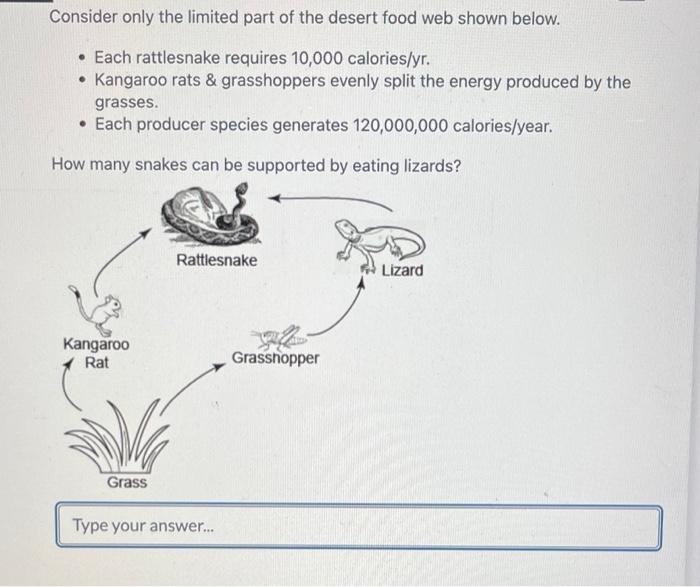
Mojave Desert Food Chain Red-Tailed Hawk (Desert USA, n.d.) Mojave Rattle Snake (Brune, 2004) Kangaroo Rat (University of California, n.d.) Creosote Bush (Hartley, 2011) Sun (Clipart Panda, 2014) Producer Consumer Consumer Consumer
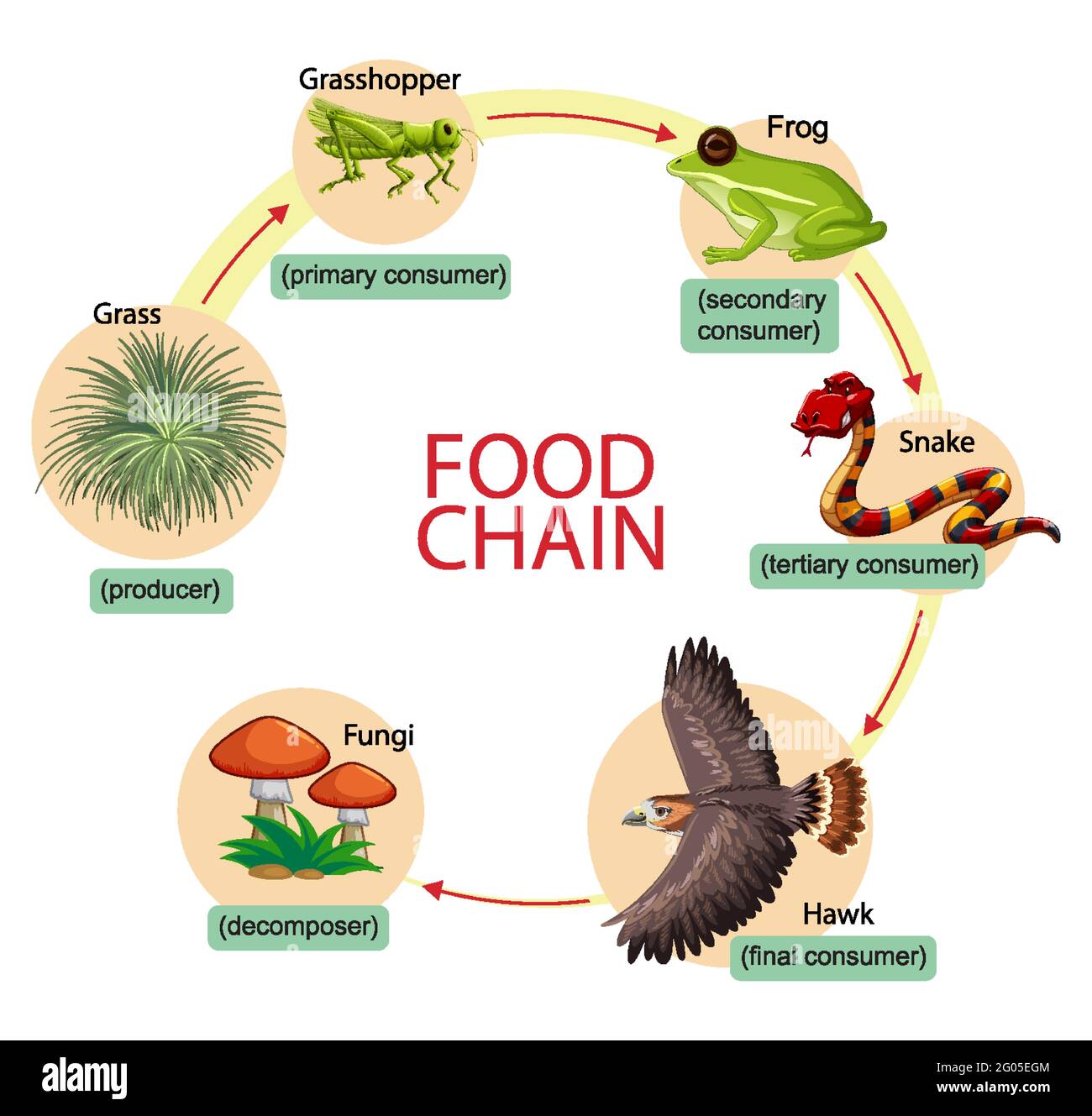
A snake, the tertiary consumer of the ecosystem, then eats the frog. Finally, the snake is consumed by a hawk, the apex consumer of the grassland ecosystem. After the hawk's death, decomposers release nutrients into the soil to be utilized by the producers. The above is an example of the food chain, which is only a part of the food web.

Desert Food Chain and Food Web Biology Diagrams
In a desert ecosystem, a secondary consumer may be a snake that eats a mouse. In underwater kelp forests, sea otters are secondary consumers. This way, the food chain is able to continue. As an example, grass produces its own food through photosynthesis. A rabbit eats the grass and then a fox eats the rabbit.

A food chain is a series of organisms each dependent on the next as a source of food. This simple definition encapsulates the essence of a food chain, highlighting the direct and linear relationship between different organisms within an ecosystem. Also Read: The Magic of Photosynthesis: How Plants Make Food. Food Chain Types