Insect Diagram Stock Illustrations 627 Insect Diagram Stock Biology Diagrams Insects appear on the highest levelof the food chain: they classify as primary or secondary decomposers, depending on the species, and help to break down organic material such as wood, leaves and plants. Insects consume dead and decaying matter, essentially recycling remains back into the Earth, and serve as food for many other animals on the food chain too. They follow consumers on the food Insects in Food Chains: Fact: These ants "farm" aphids who get food by sucking the sap from plants. They give some of this to ants in the form of honeydew in. oumnh.ox.ac.uk: Eat and be eaten: the fundamental role of insects in … Insects occupy essential positions in the food chain. The grasshopper eats the plant, the bird eats the
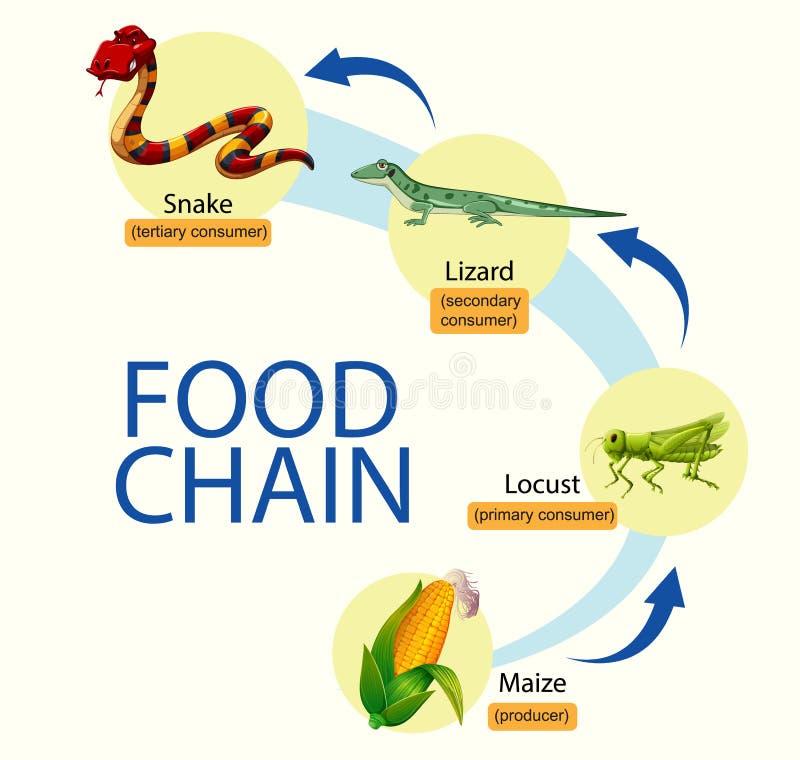
The insect food chain is a complex network of interconnected organisms, each playing a vital role in the ecosystem. Plants, as producers, convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Herbivores (primary consumers) feed on plants, while carnivores (secondary consumers) hunt and eat herbivores. At the top of the food chain, apex predators control populations of other animals. The insect food chain is a complex web of interconnected species, spanning from primary consumers (herbivores) to tertiary consumers (omnivores). Herbivores feed on plants, while carnivores prey on other insects. Omnivores, such as ants and cockroaches, consume both plant and animal matter. Decomposers play a crucial role in nutrient recycling by breaking down dead organisms.

Where Are Insects On The Food Chain? Biology Diagrams
The fast growing of the world population and scarcity of resources coupled with climate change necessitate the search for cheap and sustainable source of food as alternative to the conventional

Insects and insect-products might lead to a more sustainable food supply chain. Insects are the sole food source for many amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, making their roles in food chains and food webs extremely important. It is possible that food webs could collapse if insect populations decline.

The Intricate Insect Food Chain: Understanding the Balance of Ecosystems Biology Diagrams
Why are insects important in the food chain? They provide amphibians, reptiles, birds and some mammals with a critical source of food. Some humans also consume insects, and use insect parts for economic and social activities. Insects play critical roles in plant and flower life. What kind of food does an insect eat? Insect protein has high-quality properties and can be used as an alternative source of protein throughout the food chain, from feed for aquaculture to ingredients for nutritional supplements for humans and pets. All animal species, regardless of their diet, eat insects in their natural diet. allow us to amplify the central role of insects Insects are part of the traditional diets of approximately 2 billion people worldwide. Insects can contribute to food security and be a part of the solution to protein shortages, given their high nutritional value, low emissions of greenhouse gases, low requirements for land and water, and the high efficiency at which they can convert feed into food.

Insects play a crucial role in the food chain, consuming dead and decaying matter to recycle remains back into the Earth. They serve as food for many other animals on the food chain, which derive energy from producers like plants and fungi. Insects can contribute to food security and be part of the solution to protein shortages due to their
